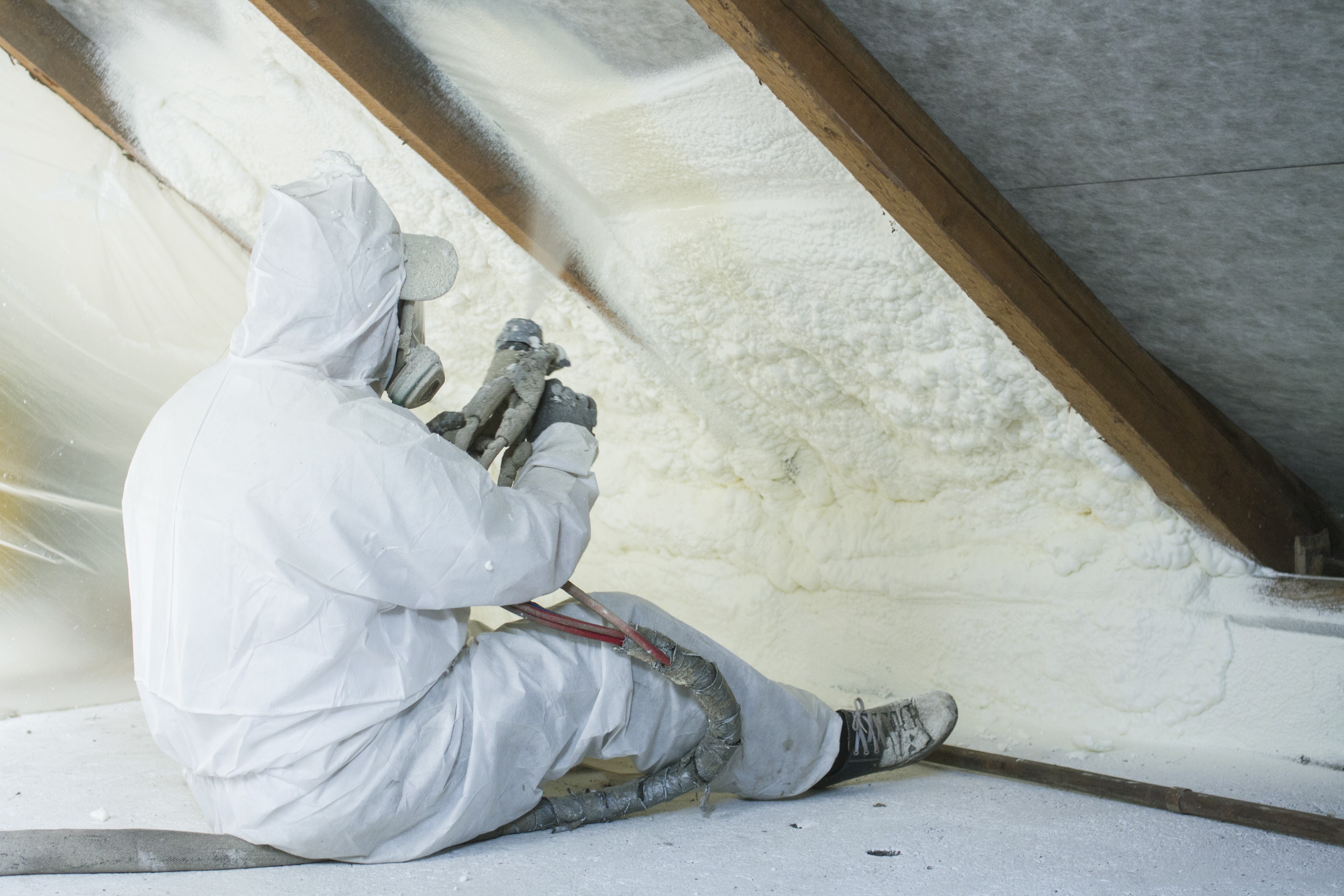
On-site testing of spray applied polyurethane foam (spf)
Introduction
Application of new and existing roofing systems consisting of spray applied polyurethane foam (SPF) should currently meet ASTM standards. These are either ASTM D 5469 for new systems or a proposed new standard from ASTM for coverings applied over existing roofing systems. These standards outline general procedures and precautions necessary for proper and safe application of SPF roofing systems.
A common aspect of the standards is sampling and testing. It states that two core samples should be taken for the first 10, 000 square feet of roof area and one sample for each additional 10, 000 square feet or fraction thereof.
These core samples must be tested for foam thickness, lift thickness, compressive strength (ASTM D 1621), density (ASTM D 1622), and cell structure (ASTM D 2856).
The ASTM tests listed above are designed to be laboratory tests. With traditional methods, SPF must be sprayed on-site, core samples taken and forwarded to a laboratory at a remote location for testing.
Often, this laboratory is the in- house testing facility of the manufacturer of the product being tested. Not only does the testing require at least a couple of days (during which time the applicator continues to apply the product), but with the manufacturer testing his own material conflict of interest issues arise.Field confirmation that the core sample meets the manufacturer’s published specification values for compressive strength is a reasonable indicator that the formulation is within the manufacture’s limits as applied.
An on-site test method eliminates transit time required for testing of samples and substandard roofing systems can be identified immediately.
In addition, according to ASTM D 5469, the entire roof must be sprayed before samples can be taken and substandard material identified.
At this point the roofing system must be completely replaced at enormous cost.
With a field compression test, a small sample could be sprayed and allowed to set.
The compressive strength of the SPF could be measured immediately and, if passing project’s or manufacture’s requirements, be applied to the entire area.
Core samples should be taken and tested during and upon completion of the application as well.
On-site Testing
A field test is available to measure the compressive strength of spray applied polyurethane foam shortly after installation, allowing for appropriate curing time. To be widely accepted in the industry, this testing device and procedure must use proven testing technology; be simple and easy to use; be inexpensive; and be portable for use in the field. As called out in the ASTM application guide, the on-site testing device approximates ASTM D 1621 “Standard Test Method for Compressive Properties of Rigid Cellular Plastics”. The device must have repeatable results that can be correlated to data reported from laboratory testing.
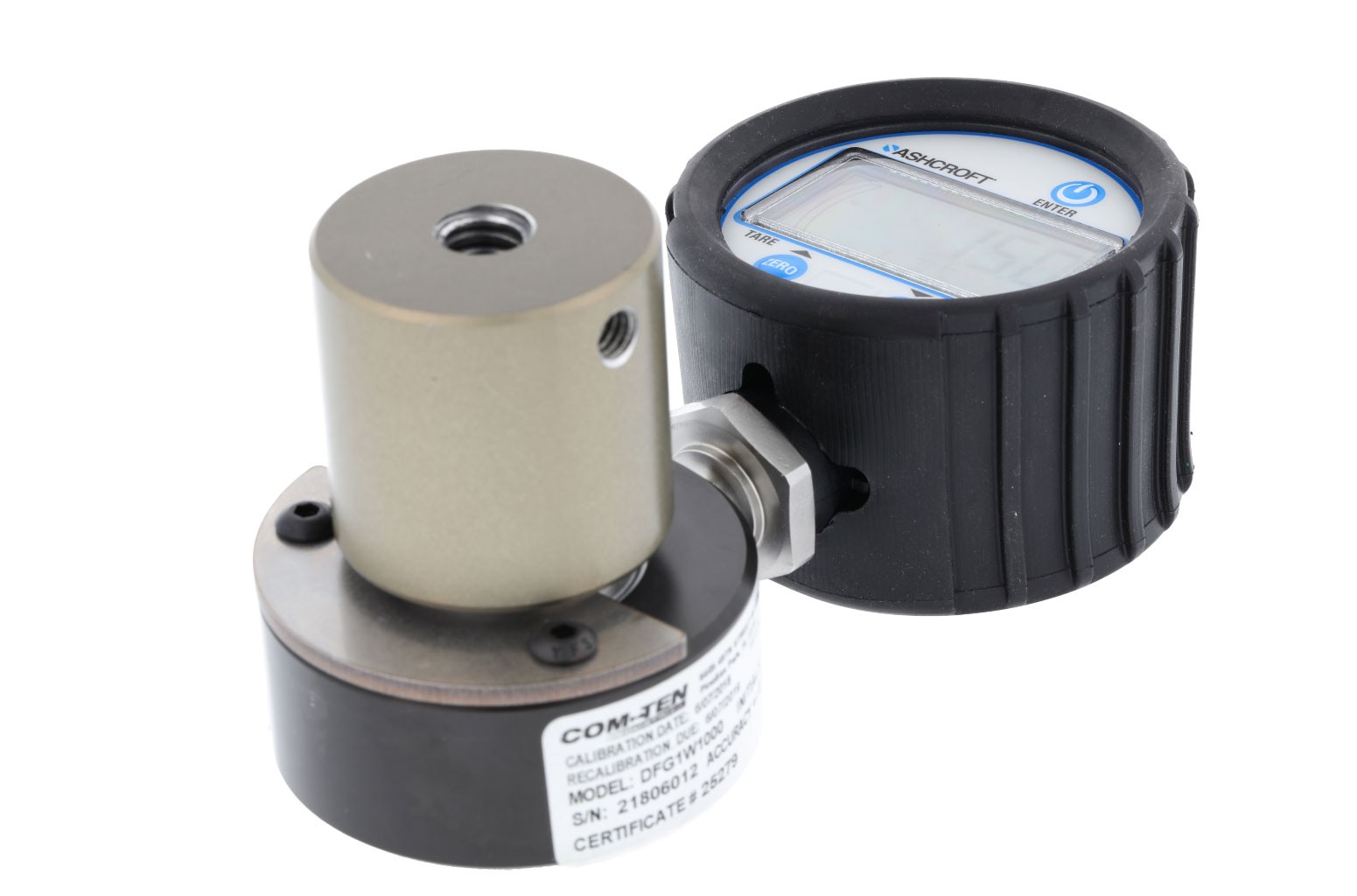
A field device with a calibrated and traceable force gauge would be suitable for generating accurate and repeatable results ASTM D 1621 allows for the use of a 4 square inch core sample (2.25 inch diameter) of at least 1 inch thickness. To achieve best results, the top and bottom of the sample should be flat, parallel, and free of defects or flaws. A 2.25 inch diameter core is the size of the sample recommended to be used in the field equipment, a Portable Foam Compression Tester. This hand operated tester has a single arm crank that can be rotated at a slow, deliberate rate to approximate the constant rate of motion that would be used in a laboratory.
After application of the SPF to a small area, core samples are be taken with a standard size core cutter. The core sample is trimmed flat and parallel and placed in the Portable Foam Compression Tester. The operator compresses the sample at a constant rate of approximately 5 revolutions per minute, which relates to a crosshead speed of 0.5 inch/min. While continuing to compress the sample, the movement of the force gauge is closely watched. The force continues to rise until it levels off at the material’s yield point. At this point the force ceases to increase (or increase very slowly) while the sample continues to be compressed. This is the yield, or primary failure, point of the material. If the material continues to be compressed, the force will begin to increase after a time. At this point the test is stopped and the yield point recorded. The yield point, as read on the force gauge, must be divided by the cross sectional area to obtain the yield strength in psi (lb/sq. inch). see also the article "from PSI to LBS "
Example: If you have a 4 square inch sample (2.25 inch diameter) that had a gauge reading of 100 pounds as its yield point, the yield strength (or compressive strength) of the foam would be 25 psi.
When the results obtained through the use of the field tester indicate a lower compressive strength value than specified by the SPF manufacturer, further testing and corroboration by means of laboratory testing are warranted before the application is allowed to proceed.
Comparison Testing
In order for the field testing of SPF to be viable and accepted in the industry, it must be correlated to laboratory results achieved with ASTM D 1621. A study was performed to compare field testing using the Portable Foam Compression Tester to laboratory results using a constant rate of motion compression test system. Sixty (60) core samples of 2.25 inch diameter (with similar ages and densities) were randomly taken from the same application of spray applied polyurethane foam. The laboratory tests were run on a compression tester at a crosshead speed of 0.5 inch/minute, and the yield point was automatically detected. Compressive strength tests were performed on the Portable Foam Compression Tester to determine the material’s yield point using the procedures in the above section. The thickness of each sample was measured and thirty (30) tests were performed by each method.
Correlation to Laboratory Results
The results of the comparison testing are shown in Figure 7. Average sample thickness for the tests was nearly equal, 2.06 vs. 2.05 inch. Force results from the tests show that the SPF had an average compressive strength of 20.43 psi when tested in laboratory conditions and 20.77 psi when tested with the field equipment. Results from the field tests averaged 1.7% higher than lab tests. The standard deviations of the test results were between 2.5 and 3 psi. Distribution of the compressive strength in relation to the sample thickness for the laboratory results and field testing were very similar. These results show that the field tests performed with the Portable Foam Compression Tester are moderately comparable with those done in the lab following ASTM D 1621.
In addition to the test results shown in this report, corroboration between the field and lab test procedures has been studied by various entities. Field units were tested by the Performance Based Studies and Research Group (PBSRG) at Arizona State University, Del E. Webb School of construction. Results compiled from the testing, during which similar samples were tested by both the field device and laboratory machines, have established a relationship between the two types of testing. It was noted that these results typically vary less than 10% among the field and lab testing.In addition to the test results shown in this report, corroboration between the field and lab test procedures has been studied by various entities. Field units were tested by the Performance Based Studies and Research Group (PBSRG) at Arizona State University, Del E. Webb School of construction. Results compiled from the testing, during which similar samples were tested by both the field device and laboratory machines, have established a relationship between the two types of testing. It was noted that these results typically vary less than 10% among the field and lab testing.
Summary
The field compressive strength tests performed with the Portable Foam Compression Tester gives moderately comparable results to those done in the laboratory. When used in conjunction with recommended application guides and procedures, the field test will improve the quality of the SPF installations by immediately identifying substandard compressive strength of installed materials. The field compression test is not meant to solely replace an experienced applicator’s visual inspection, “foot feel”, or density check. Nor does it take into account the difference in curing times between samples tested on side versus those tested in the lab. It is another analytical tool available that can identify substandard SPF installations on site. This allows for laboratory testing to be done and corrective action to be taken before the entire installation in complete, thus saving both time and money.The field compressive strength tests performed with the Portable Foam Compression Tester gives moderately comparable results to those done in the laboratory. When used in conjunction with recommended application guides and procedures, the field test will improve the quality of the SPF installations by immediately identifying substandard compressive strength of installed materials. The field compression test is not meant to solely replace an experienced applicator’s visual inspection, “foot feel”, or density check. Nor does it take into account the difference in curing times between samples tested on side versus those tested in the lab. It is another analytical tool available that can identify substandard SPF installations on site. This allows for laboratory testing to be done and corrective action to be taken before the entire installation in complete, thus saving both time and money.
Details test results
| LABORATORY RESULTS | FIELD RESULTS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample # | HEIGHT (in) | YIELD (lb) | STRENGTH (psi) | HEIGHT (in) | YIELD (lb) | STRENGTH (psi) |
| 1 | 2 | 82.2 | 20.6 | 2 | 104 | 26.0 |
| 2 | 2 | 74.5 | 18.6 | 2.5 | 86 | 21.5 |
| 3 | 2.25 | 85.3 | 21.3 | 2 | 72 | 18.0 |
| 4 | 1.875 | 69.4 | 17.4 | 2.125 | 80 | 20.0 |
| 5 | 1.875 | 83.9 | 21.0 | 2.125 | 74 | 18.5 |
| 6 | 2 | 67.4 | 16.9 | 2.125 | 80 | 20.0 |
| 7 | 1.875 | 73.8 | 18.5 | 2 | 76 | 19.0 |
| 8 | 2 | 94.2 | 23.6 | 2.375 | 82 | 20.5 |
| 9 | 1.625 | 95.3 | 23.8 | 1.875 | 72 | 18.0 |
| 10 | 1.875 | 72.0 | 18.0 | 1.75 | 86 | 21.5 |
| 11 | 2.125 | 91.4 | 22.9 | 1.75 | 100 | 25.0 |
| 12 | 1.75 | 76.5 | 19.1 | 2.25 | 80 | 20.0 |
| 13 | 2 | 97.1 | 24.3 | 2.5 | 98 | 24.5 |
| 14 | 2.25 | 78.1 | 19.5 | 2 | 84 | 21.0 |
| 15 | 2.5 | 81.8 | 20.5 | 2 | 68 | 17.0 |
| 16 | 2.375 | 81.5 | 20.4 | 2.125 | 92 | 23.0 |
| 17 | 2.5 | 90.1 | 22.5 | 2.25 | 92 | 23.0 |
| 18 | 1.75 | 88.2 | 22.1 | 2.5 | 88 | 22.0 |
| 19 | 1.75 | 102.4 | 25.6 | 1.875 | 64 | 16.0 |
| 20 | 2 | 72 | 18.0 | 2 | 72 | 18.0 |
| 21 | 2 | 69 | 17.3 | 1.75 | 108 | 27.0 |
| 22 | 2 | 93 | 23.3 | 1.625 | 92 | 23.0 |
| 23 | 2.375 | 72.7 | 18.2 | 2.125 | 68 | 17.0 |
| 24 | 2.5 | 77.5 | 19.4 | 2 | 70 | 17.5 |
| 25 | 2.125 | 82.2 | 20.6 | 1.625 | 92 | 23.0 |
| 26 | 2 | 67.0 | 16.8 | 2.2125 | 72 | 18.0 |
| 27 | 2.125 | 94.4 | 23.6 | 2 | 84 | 21.0 |
| 28 | 2.25 | 63.8 | 16.0 | 2.25 | 96 | 24.0 |
| 29 | 1.875 | 81.4 | 20.4 | 1.875 | 72 | 18.0 |
| 30 | 2.125 | 93.9 | 23.5 | 2.125 | 88 | 22.0 |
| AVG | 2.06 | 81.73 | 20.43 | 2.05 | 83.07 | 20.77 |
| STD DEV | 0.23 | 10.45 | 2.61 | 0.24 | 11.58 | 2.89 |
How Com-Ten can assist with anchor and adhesion testing
At Com-Ten, we specialize in anchor and adhesion testing, ensuring your projects meet the highest safety and structural standards. Our team is fully trained to Standards and boast extensive expertise in regulations.
Here’s how we can help:
- Precision Testing: We utilize advanced techniques to perform accurate pull tests, identifying the strength and reliability of your anchors.
- Certificate of calibration: All our pull testers come with a recent certificate of calibration included data measurement to achieve full compliance with industry standards, minimizing risks.
- Availability: Our pull testers and accessories are in stock and ready to be shipped for your next job to be done.
If you have any questions about our anchor or adhesion testers or need more details about what we offer, feel free to reach out to us. We’re here to support your project's success.
Linked products
test-equipment-for-adhesion-tests-on-membrane-or-spf-in-construction
ADHOR D : Digital adhesion tester with disposable discs- Measure pull out strength between two layers after a repair or new work ...
test-equipment-for-adhesion-tests-on-membrane-or-spf-in-construction
SPUKIT :Sprayed Polyurethane Foam testing kitComplete kit for foam testing
test-equipment-for-adhesion-tests-on-membrane-or-spf-in-construction
ADHOR RA : Analog Adhesion Tester with 2.25" disposable discs & 4" reusable disc- Includes a pack of 10 disposable discs and 1 reusable disc
- Displays...